Overview of On-Premises ENTERPRISE
Styra Declarative Authorization Service (DAS) is composed of multiple microservices running on a Kubernetes cluster. Styra DAS has a single microservice responsible for receiving the incoming network requests called Gateway. A Gateway runs a single Kubernetes pod and receives the requests from Kubernetes ingress. The Gateway delegates its handling to the relevant microservice running on a Kubernetes pod.
This page describes how to obtain the Styra Docker images, Styra DAS architecture, and how microservices are integrated.
Prerequisites
-
Confirm Docker is installed.
-
Download the configuration files using the following link: on-prem-assets.
-
Extract the files to a local directory using
tar xzf on-premises.tar.gz. -
Set up the credentials to pull the images for Styra's Docker registry.
-
Export the environment variable
ON_PREMISES_VERSIONto ensure that the commands mentioned in this guide refer to the correct version.
export ON_PREMISES_VERSION=0.9.0Obtain the Microservice Images
Styra DAS microservices are packaged as Docker images. These images are distributed through a Docker registry hosted at registry.styra.com. Configure your Kubernetes cluster to pull the images directly from Styra or you can download, re-tag, and push them to an internal Docker registry.
The registry at registry.styra.com requires authentication.
-
important
The generated token should not have any path restrictions. The API token requires path = ".*".
-
Login to
registry.styra.comusing the standarddocker logincommand. -
Enter your credentials:
-
Username:
<das-id>.styra.com. -
Password: Use the token secret (previously generated).
For example:
> docker login registry.styra.com
Username: <das-id>.styra.com
Password: <paste token secret> -
To use the images directly from registry.styra.com, you will need to configure Kubernetes to use a private registry using those authentication credentials. Now, set the REPOSITORY_URL environment variable as follows for the rest of the Styra DAS installation.
export REPOSITORY_URL="registry.styra.com"
(Optional) Push Styra Images to an Internal Registry
Once authenticated, use the following command to pull the Styra images to your local Docker registry.
export STYRA_SERVICES=("activity" "agentbundle" "agentloader" "agentstatus" "agentstatusstore" "analysis-api" "blueprints" "coordinator" "datasources" "environment-configurator" "fetchdb" \
"gateway" "logreplay" "mock-opa" "policies" "stacks" "systems" "tenants" "timeseries" "ui")
for SERVICE in "${STYRA_SERVICES[@]}"
do
docker pull registry.styra.com/styra/$SERVICE:on-prem-${ON_PREMISES_VERSION}
done
Re-tag images with your Docker registry hostname and push them to your registry:
-
Login to your registry.
export DOCKER_URL="my.registry.internal"
docker login $DOCKER_URL -
Tag the Styra images.
for SERVICE in "${STYRA_SERVICES[@]}"
do
docker tag registry.styra.com/styra/$SERVICE:on-prem-${ON_PREMISES_VERSION} $DOCKER_URL/styra/$SERVICE:on-prem-${ON_PREMISES_VERSION}
done -
Push the Styra images to your internal registry.
for SERVICE in "${STYRA_SERVICES[@]}"
do
docker push $DOCKER_URL/styra/$SERVICE:on-prem-${ON_PREMISES_VERSION}
done
The following instructions install Elasticsearch and Postgres deployments:
-
Pull the Elasticsearch and Postgres images.
docker pull docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.17.5
docker pull postgres:14.5 -
Tag the Elasticsearch and Postgres images with your internal registry.
docker tag docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:7.17.5 $DOCKER_URL/elasticsearch:7.17.5
docker tag postgres:14.5 $DOCKER_URL/postgres:14.5 -
Push the Elasticsearch and Postgres images (if using the bundled Elasticsearch and Postgres).
for f in elasticsearch:7.17.5 postgres:14.5; do docker push $DOCKER_URL/$f; done -
Set the REPOSITORY_URL environment variable with the repository URL. If your
$DOCKER_URLdoes not contain "/" characters thenREPOSITORY_URLcan be set to$DOCKER_URL; otherwiseREPOSITORY_URLwill be defined with the/properly escaped.export REPOSITORY_URL="my.registry.internal\/library"
Styra DAS can be configured to use AWS storage instead of Postgres.
Architecture
The Styra DAS architecture splits the functionality across microservices which enables the Styra backend to scale individual components and adapt to varying workloads.
Figure 1 shows Styra microservices (in blue) that are made available by the Gateway API and how they relate to different entities talking to the Styra DAS over the network using OPA and the Styra DAS UI.
-
OPA: Supported system-types act as clients of the Styra DAS API. When you create and install a system, the gateway provides the API for the OPA to operate. It also provides the bundle API to OPA containers running on the cluster, and the APIs for Styra DAS receive status updates and decisions from the OPAs. These interactions and APIs are designed based on the availability after OPA has successfully downloaded the initial bundle, it can continue serving authorization requests even if the Styra DAS becomes temporarily unavailable.
-
Styra DAS UI: All Styra DAS UI interactions go through the gateway. The Styra DAS UI frontend downloads both its JavaScript through the gateway from the Styra DAS UI microservice. It also interacts with the other APIs through the gateway, in order to implement and facilitate the actions on the Styra DAS UI. Internally, the Styra DAS system relies on controllers (for example, environment-configurator) to converge the platform to a desired state. These interactions between the microservices don't require the involvement of the gateway.
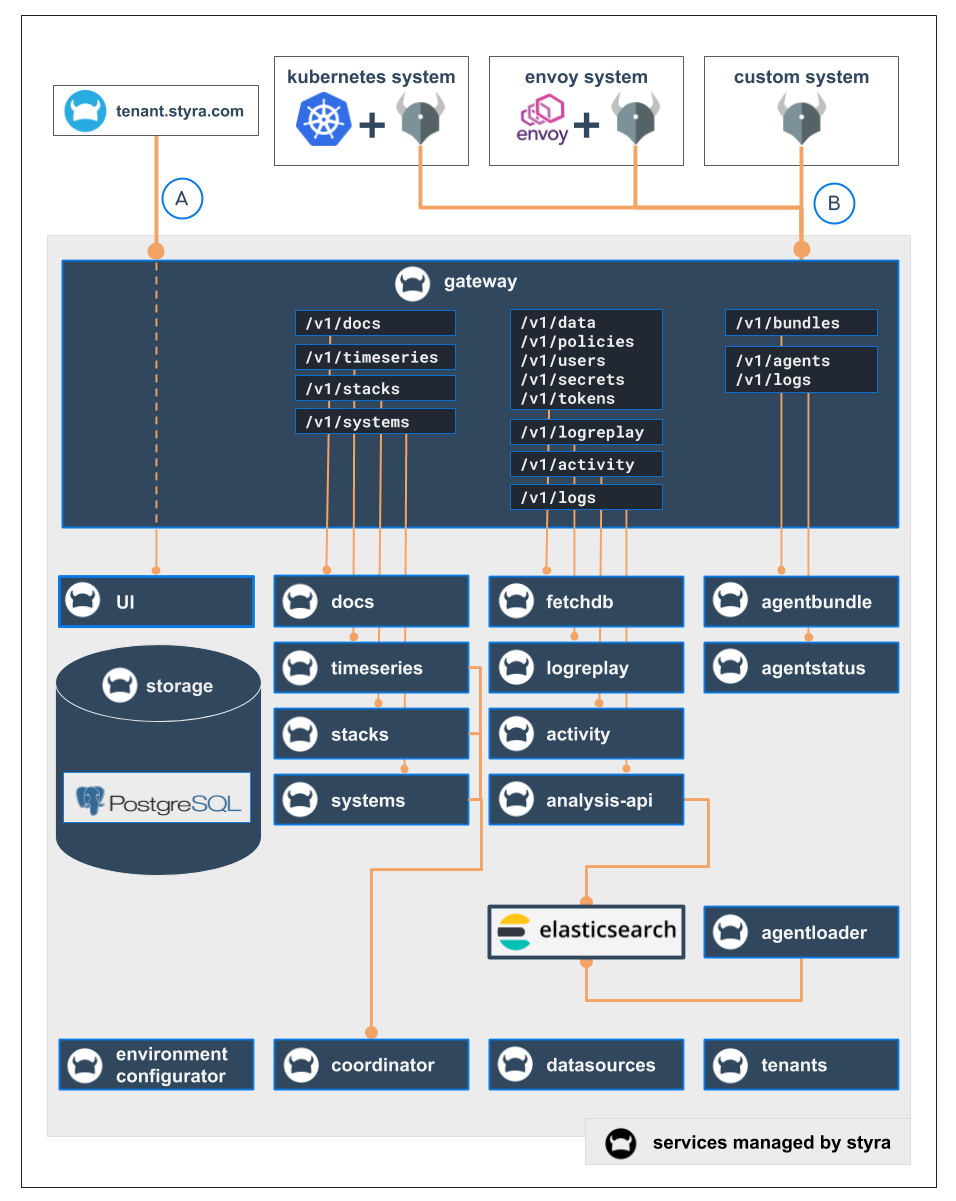 Figure 1 - Architecture of Styra DAS with Microservices
Figure 1 - Architecture of Styra DAS with MicroservicesThe communication between microservices occurs over the following protocols:
-
External communication towards (for example: bundle downloads) Styra DAS occurs over HTTPS. However, the TLS is terminated with the Kubernetes ingress.
-
Service to service communication occurs over HTTP, with the exception of the coordinator that uses gRPC with the other services.
-
Communication with storage subsystems uses their preferred protocols as follows:
- Using PostgreSQL, the protocol is PostgreSQL.
- Using Elasticsearch communication occurs using HTTP.
Styra DAS Microservices
The following table lists the various Styra DAS microservices:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| blueprints | Blueprints, required to work with Mock OPA. |
| gateway | API gateway. All API requests are routed through gateway. It enforces authentication, authorization, and records user activity. |
| gateway-alt | Optional second API gateway. |
| ui | Serves HTML and JavaScript for the Styra DAS UI. |
| docs | Serves documentation. |
| timeseries | Computes metrics over decision log APIs. |
| systems | System configuration and management APIs, OPA configuration bundle APIs used for discovery. |
| stacks | Stack configuration and management APIs. |
| fetchdb | Configuration management APIs. |
| logreplay | APIs to assess the impact of a policy change to previous decisions. |
| mock-opa | The Mock OPA service. |
| policies | APIs for policy management. |
| activity | Provides user activity log APIs. |
| analysis-api | APIs to search decision logs. |
| agentbundle | Constructs and serves policy bundles. |
| agentstatus | APIs for OPAs to send status updates and decision logs. |
| agentstatusstore | Storage for status updates and decision logs. |
| agentloader | Loads decision logs from OPA to Elasticsearch for indexing. |
| environment-configurator | Manages storage resources for the environment. |
| coordinator | Shards work across service replicas. |
| datasources | Executes data sources that require pulling data. |
| tenants | Configures and manages the tenant internal state. |
| elasticsearch | Search engine for decision logs. |
| storage | PostgreSQL for all internal, persisted states. |