Install Agents
You must install the following two main components onto your Kubernetes cluster. Each component has its own configuration.
Components on Kubernetes Cluster
- Open Policy Agent: Responsible for Admission Control decisions.
- Styra Discovery Datasource: Responsible for discovering resources on your cluster for monitoring.
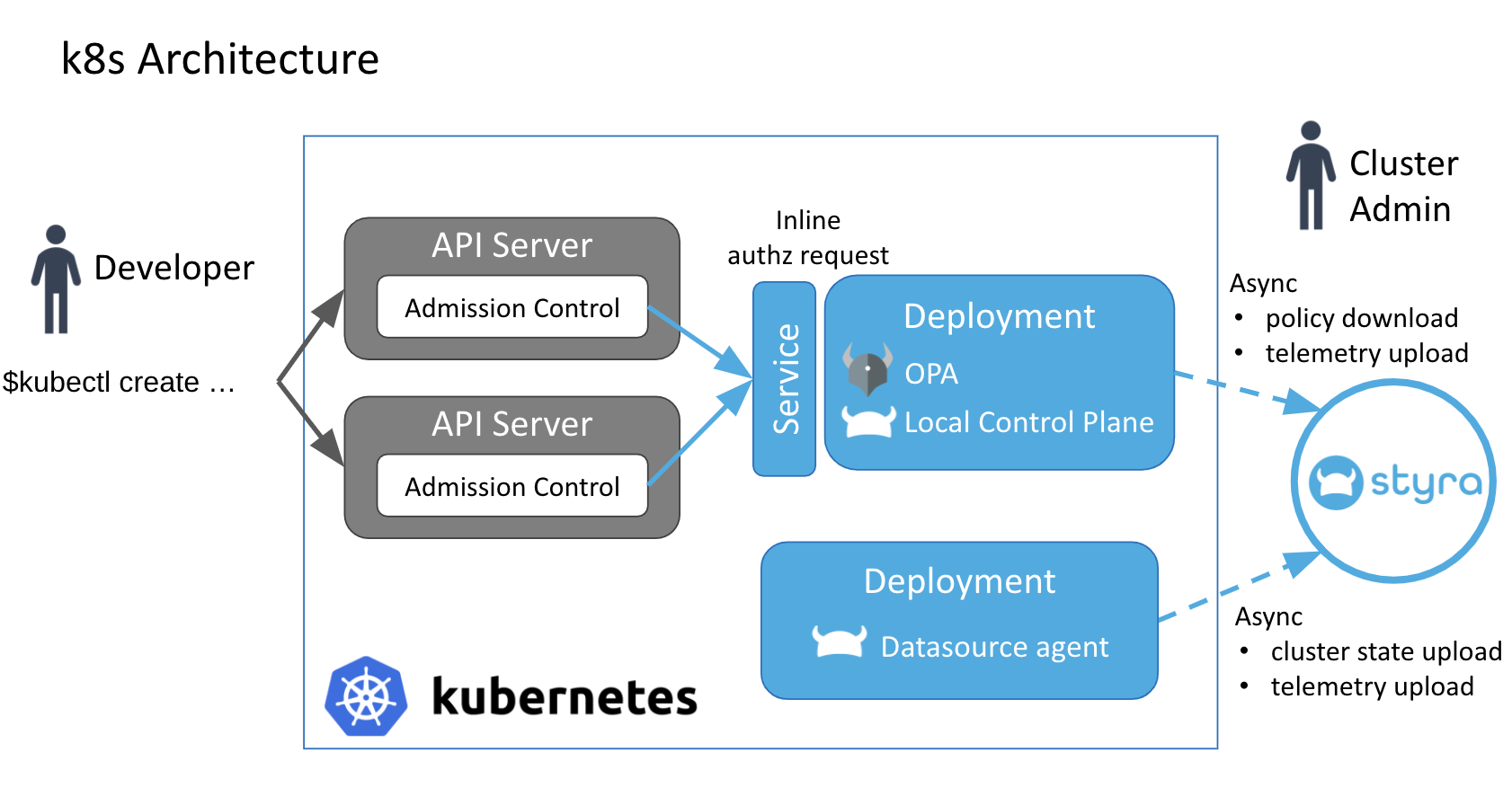 Figure 1 - Components on Kubernetes Cluster
Figure 1 - Components on Kubernetes ClusterOpen Policy Agent
The Open Policy Agent is responsible for making real-time admission control decisions within the API server. Its sidecar styra-local-plane is responsible for replicating resource metadata into OPA, so it knows what resources are available on the cluster and can enforce policies that depend on that information. The OPA website includes the authoritative guide for configuring OPA.
Styra configures OPA and styra-local-plane using the following key ideas.
- Everything besides the role-based access control (RBAC) is installed in the
styra-systemnamespace. - OPA is not configured with an authentication/authorization policy on its APIs.
- The certificates needed for OPA to talk to the Kubernetes API server are stored as Kubernetes secrets. These certificates are auto-generated by the Styra API that generates the installation instructions, and are stored on the backend. The certificates are available via the API to users with the proper permissions.
- The Bearer-token that OPA needs to talk to
styra.comis embedded into the configuration generated by the Styra API. The API regenerates that token once it expires on the next API call asking for installation instructions. styra-local-planeis grantedviewpermissions on the cluster.- The validating-webhook configuration routes all
CREATEandUPDATEcommands to OPA for all resources. - The validating-webhook configuration ignores any requests for a namespace with the label
openpolicyagent.org/webhook=ignore. One of the commands you use to install the agents sets this flag on thekube-systemnamespace. Therefore, OPA policies are not enforced onkube-system.
To retrieve the OPA configuration, run the following curl command.
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer ${STYRA_API_TOKEN}" "https://<das-id>.styra.com/v1/systems/${SYSTEM_ID}/assets/opa"
Styra Discovery Datasource
For monitoring the state of the policy, Styra provides a discovery Data source that you can install on your Kubernetes cluster. It periodically pulls all resources from the API and sends it to <das-id>.styra.com.
In future, the agent will set up watches on the Kubernetes API server, instead of periodically pulling all of the data through the API.
The following shows the key ideas of discovery data source.
- Discovery Data source is installed in the same namespace as OPA:
styra-system. - Discovery is granted the ability to read all resources and list all resource types, which requires more than the cluster-level
viewpermission.
To retrieve the datasources-agent configuration, run the following curl command.
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer ${STYRA_API_TOKEN}" "https://<das-id>.styra.com/v1/systems/${SYSTEM_ID}/assets/datasources-agent"
Install Styra on Kubernetes Cluster
The Kubernetes system installation instructions are available in <das-id>.styra.com.
Navigate to your Kubernetes system by selecting your WORKSPACE >> SYSTEMS >> Settings tab >> Install page to see the installation instructions.
Install the following two pieces of software on your cluster.
- Open Policy Agent: Handles admission control requests from the Kubernetes API Server.
styra-local-control-plane: Downloads policy from<das-id>.styra.com, discovers the Kubernetes resources those policies require, and distributes both to all replicas of OPA.
There are numerous options for installing OPA on your Kubernetes cluster as an admission controller, for example: helm, helm3, kustomize, and kubectl.
-
In the left navigation panel, click the ( ⨁ ) plus icon next to SYSTEMS.
-
Fill out the form using the following information:
- System name: A not-necessarily unique name for your cluster. The system name will appear in the left navigation panel.
- Description: A documentation string for your cluster.
- Read-only: If enabled it stops users from editing the policy for this cluster in the GUI. This is valuable if you store these policies outside the
<das-id>.styra.com, and you want to communicate with users viewing the policies outside the<das-id>.styra.cominterface.
Configure Kubernetes Environments
Different flavors of Kubernetes require changes to the default configuration.
minikube
In the Styra discovery deployment specification, you can remove the liveness and readiness probes, as shown in the following configuration file.
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health
scheme: HTTPS
port: 443
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 5
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health
scheme: HTTPS
port: 443
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 5
Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Modify the OPA deployment file for AKS after you run the deployment and edit the OPA deployment in the styra-system namespace. In the specification, you can remove the tolerations and affinity clause, as shown in the following configuration file.
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
operator: Exists
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
Perform the following steps in the data sources deployment specification:
- Delete the ClusterRole named
read-all-global. - Delete the ClusterRoleBinding named
datasources-agent-read-all. - Add the following ClusterRoleBinding:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: root-cluster-admin-binding
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: default
namespace: styra-system
In the OPA deployment specification, you can remove the tolerations and affinity clause, as shown in the following configuration file.
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
operator: Exists
AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS)
For EKS both the default datasources-agent and OPA deployment configuration must be modified, after you run them (default datasources-agent and OPA deployment) and edit the default datasources-agent and OPA deployment in the styra-system namespace.
In the Data sources deployment specification, you can remove the liveness and readiness probes, as shown in the following configuration file.
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health
scheme: HTTPS
port: 443
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 5
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /health
scheme: HTTPS
port: 443
initialDelaySeconds: 10
periodSeconds: 5
In the OPA deployment specification, you can remove the tolerations and affinity clause, as shown in the following configuration file.
tolerations:
- effect: NoSchedule
key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
affinity:
nodeAffinity:
requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
operator: Exists
Configure Data Source Agents
Each Kubernetes system has a Kubernetes data source associated with it. The ID of that data source is systems/{SYSTEMID}/kubernetes/resources which is returned when you query systems API for each system. The data source APIs work with data sources. For example, the following is displayed when you query the systems API and click on the data source resources on the Kubernetes system (/v1/datasource/{datasourceID}).
{
"request_id": "7af08205-fd61-4f86-863e-1447fa664cda",
"result": {
"category": "kubernetes/resources",
"id": "systems/cf8d422d77e943c4a09c75236cd1630f/kubernetes/resources",
"metadata": {
"created_at": "2019-06-27T22:32:38.64727557Z",
"created_by": "support@styra.com",
"created_through": "access/styra/automation",
"last_modified_at": "2019-06-27T22:32:38.64727557Z",
"last_modified_by": "support@styra.com",
"last_modified_through": "access/styra/automation"
},
"namespaces": {
"kube-system": false
},
"on_premises": true,
"status": {
"code": "finished",
"message": "",
"timestamp": "2021-03-03T23:01:11Z"
}
}
}
The following shows the structure of the data source agents configuration file:
datasources:
the/datasource/ID1: # datasource ID
selectors: # field selectors per resource [group]
# resource can be specified as
# * resource name (for example, `pods`)
# * group/resource (for example, `argoproj.io/workflows`)
# * group/version/resource (`apps/v1/daemonsets`, `/v1/services`)
# * wildcard: "*"
pods: "status.phase!=Running,spec.restartPolicy=Always" # https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/working-with-objects/field-selectors/
ingress: metadata.namespace==default
masks: # strip out resource properties given their relative path
pods:
- spec.afinity
- spec.livenessProbe
- status
- metadata.annotations["kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration"]
- spec.template.spec.containers[_].env
- spec.template.spec.containers[0].env
argoproj.io/workflows:
- "*" # exclude the entire resource type
namespaces: # allows to include/exclude namespaces
nsName: true # false to exclude, true to include
"": false # empty string means cluster-level resources
"*": false # default decision, true if not specified
The following shows an example of a data source configuration file:
{
"category": "kubernetes/resources",
"on_premises": true,
// Append configuration here.
"namespaces": {
"*": true
}
}
To change the configuration, use PUT /v1/datasources/{datasourceID} within the body of the Data source configuration file. You can override the configuration stored in DAS through the Kubernetes datasources-agent-config configuration map. Any configuration option defined there for a data source will override anything defined on the DAS side. It is preferred to configure the data source through DAS, but in certain cases some configuration information cannot leave the cluster.
Disconnect a Cluster
To disconnect a cluster, you must first uninstall the agents from the cluster. Then you can delete the Styra system that you created for that cluster.
Uninstall the Agents
Do not delete the System until you uninstall the agents.
To uninstall the Open Policy Agent, styra-local-plane, and Styra's discovery/datasource agent, you must download and execute the kubectl command.
Styra DAS UI
You can find the uninstall command in the Systems Settings page under the Uninstall section.
Styra CLI
By default, the Styra CLI shows all the Systems. Run the following command to get all the Systems.
styra get systems
Run the following command to view the details of the system using the -o yaml flag.
styra get system cc0de17f992249a6b2afd65733d09d55 -o yaml
The following result displays the uninstall command.
uninstall:
"kubectl": "curl -H 'Authorization: Bearer ...' 'https://<das-id>.styra.com/v1/systems/cf8d422d77e943c4a09c75236cd1630f/kubernetes/kubectl-all' | kubectl delete -f -"
Execute the following command to uninstall the agents.
curl -H 'Authorization: Bearer ...' 'https://<das-id>.styra.com/v1/systems/cf8d422d77e943c4a09c75236cd1630f/kubernetes/kubectl-all' | kubectl delete -f -
When you want to disconnect a cluster, you must remember to set kubectl to the corresponding context.
Delete the Styra System
To delete the Styra system, you can use either the GUI or CLI method as follows.
GUI
- In the left navigation panel, under SYSTEMS, click the name of the cluster you want to disconnect.
- Click Settings tab.
- Click trash can 🗑 icon in the lower left corner of the GUI.
CLI
Run the following command to delete a system with a specific ID.
styra delete systems <id>
The following example deletes the system with ID = e52999220c13470f8dbbfade4a194ad5.
styra delete systems e52999220c13470f8dbbfade4a194ad5