Install the Kuma Example Application
Be sure kubectl is configured to point to the cluster which has Kuma controller deployed.
To install Styra on Kuma, you must copy and paste all the three installation command from SYSTEMS >> Settings >> Install for your Kuma system into your terminal. This configures Kuma Proxy template and Kuma controller. Enable Kuma sidecar-injection on the default namespace and deploy Styra Local Plane (SLP). For custom namespace, make sure Kuma sidecar-injection is enabled and deploy SLP accordingly.
The Kuma system Quick Start provides the link to install example application. It consists of the following components which should now be running in your minikube. All resources are suffixed by the SYSTEM ID to mark them as unique.
-
example-app: A simple HTTP web server that allows employees of a hypothetical organization to obtain salary details at the path
/finance/salary. It also exposes a path/hr/dashboardthat is only accessible by employees who are part of HR. Functionally, it is a simple echo server that returns a HTTP 200 response with a plain/text body which contains a success or error message. -
client-load: A simple shell script that generates some pre-configured HTTP GET requests to test the behavior of the deployed policy. It helps generate data to visualize the impact of the configured egress and ingress policies by simulating traffic to the example-app.
-
slp: Styra Local Plane (SLP) is a service that acts as an intermediary between the OPAs and Styra DAS. OPAs are configured to retrieve bundles from SLP rather than directly from DAS. This increases availability as SLP fetches bundles from Styra DAS and persists them to disk, so policies are still available to new or restarted OPAs even if Styra DAS is unavailable.
-
Each application has two sidecar containers - Kuma data plane and OPA.
When you run the Kuma example application, the OPA sidecar will pull down the policy from DAS tenant and start enforcing it. This process takes few minutes to complete.
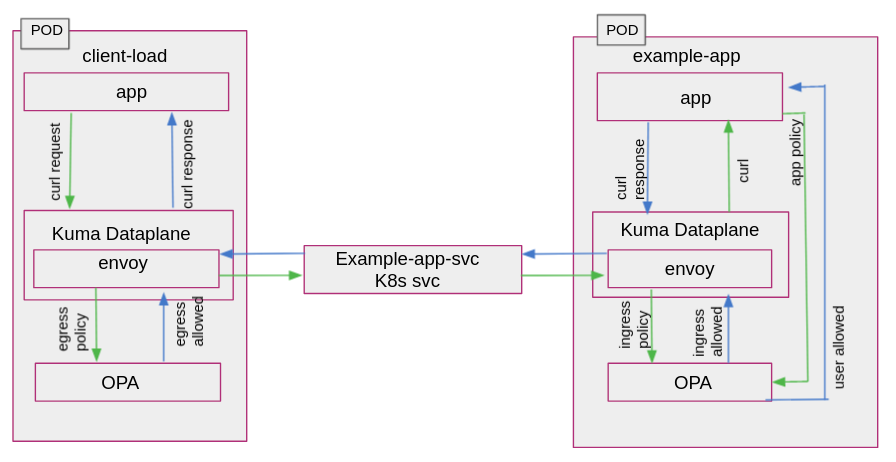 Figure 1 - Kuma Example Application
Figure 1 - Kuma Example Application